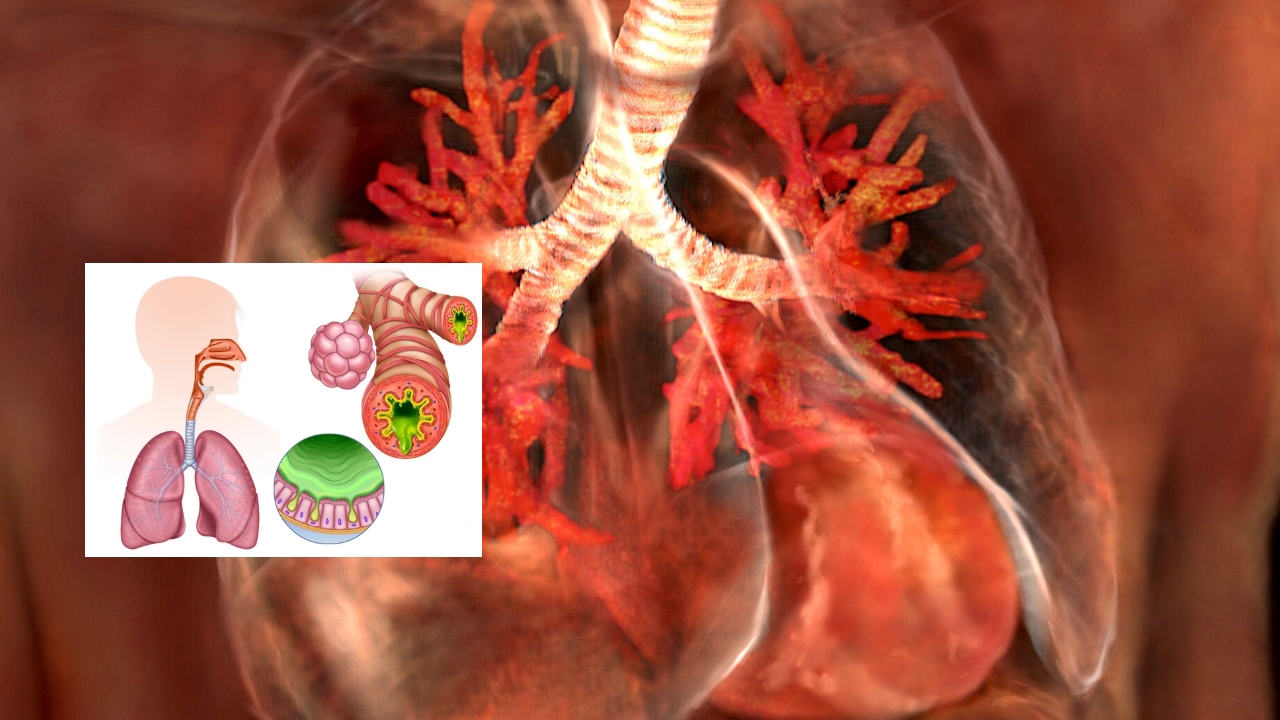
Bronchitis is a respiratory condition characterized by the inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from the lungs. It can be classified into two main types: acute bronchitis and chronic bronchitis. Understanding whether bronchitis is contagious is essential for preventing its spread and managing symptoms effectively.
Types of Bronchitis
1. Acute Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is usually caused by viral infections, similar to those that cause the common cold or flu. It typically develops following an upper respiratory infection and can last for a few days to a couple of weeks. Symptoms often include:
Cough
Mucus production
Fatigue
Shortness of breath
Mild fever
2. Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition often associated with smoking or prolonged exposure to irritants such as air pollution or chemical fumes. It is characterized by a persistent cough that produces mucus for at least three months over two consecutive years. Symptoms include:
Chronic cough
Increased mucus production
Wheezing
Shortness of breath
Is Bronchitis Contagious?
Acute Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is primarily caused by viral infections, which can indeed be contagious. The viruses responsible for acute bronchitis can spread through:
Airborne droplets: When an infected person coughs or sneezes, droplets containing the virus can be inhaled by others.
Direct contact: Touching surfaces contaminated with the virus and then touching the face, especially the mouth, nose, or eyes, can also lead to infection.
Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis, on the other hand, is not contagious. It is a result of long-term exposure to irritants, and while it may occur in individuals with a history of smoking or environmental exposure, it does not spread from person to person.
Prevention Strategies
To minimize the risk of contracting or spreading acute bronchitis, consider the following preventive measures:
- Good Hygiene Practices:
- Wash hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
- Use hand sanitizer when soap is not available.
- Avoid Close Contact:
- Stay away from individuals exhibiting symptoms of respiratory infections.
- Maintain a safe distance from those who are coughing or sneezing.
- Vaccination:
- Get vaccinated against influenza and pneumonia, as these infections can lead to bronchitis.
- Avoid Smoking and Irritants:
- If you smoke, seek help to quit.
- Limit exposure to air pollution and occupational irritants.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience symptoms of bronchitis, especially if you have difficulty breathing, a persistent cough with blood, or symptoms lasting more than three weeks, it’s important to seek medical advice. A healthcare provider can determine the appropriate treatment and whether further investigation is necessary.
Conclusion
In summary, acute bronchitis can be contagious due to its viral origins, while chronic bronchitis is not. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for effective prevention and management. By practicing good hygiene and being aware of your surroundings, you can help reduce the risk of bronchitis and other respiratory infections.
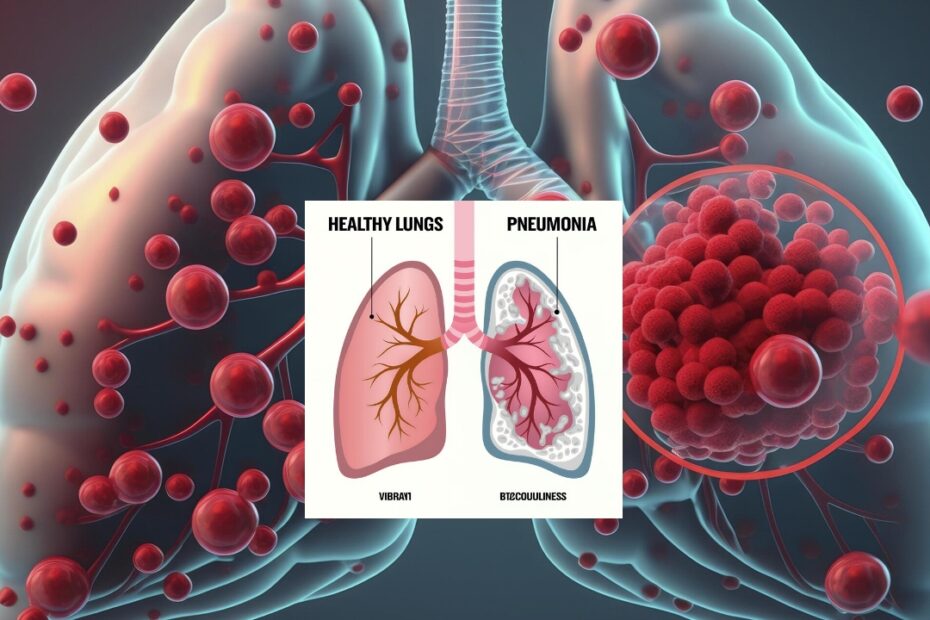
Health Talk : Is Pneumonia Contagious?
![]()