Pneumonia is a serious respiratory infection that affects the lungs and can lead to significant health complications. Understanding whether pneumonia is contagious is vital for preventing its spread and protecting vulnerable populations.
What is Pneumonia?
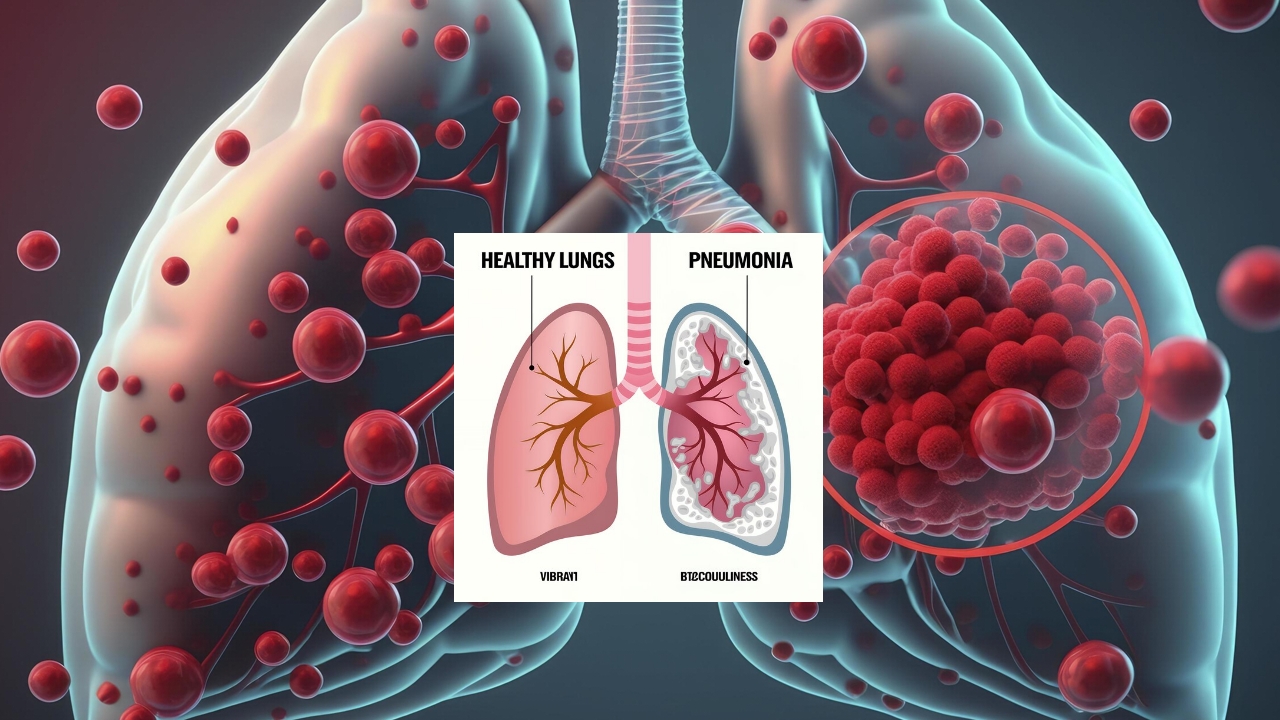
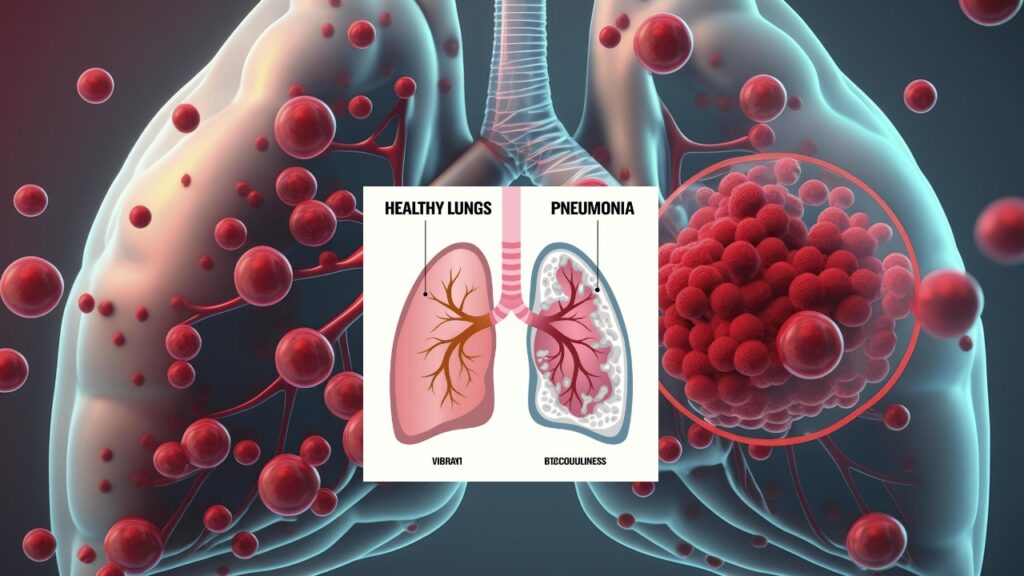
Pneumonia is characterized by the inflammation of the air sacs in the lungs, which may fill with fluid or pus, making it difficult to breathe. It can be caused by various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Symptoms often include:
Cough (with or without mucus)
Fever and chills
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Fatigue
Types of Pneumonia
1. Bacterial Pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia is often caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae but can result from other bacteria as well. This type can be serious and may require antibiotics for treatment.
2. Viral Pneumonia
Viral pneumonia is usually caused by viruses such as influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), or coronaviruses. It tends to be less severe than bacterial pneumonia but can still lead to significant health issues, especially in young children and the elderly.
3. Fungal Pneumonia
Fungal pneumonia is less common and typically occurs in individuals with weakened immune systems. It can be caused by fungi found in the environment.
Is Pneumonia Contagious?
Bacterial and Viral Pneumonia
Both bacterial and viral pneumonia can be contagious. The pathogens that cause these types of pneumonia can spread from person to person through:
- Airborne droplets: When an infected person coughs or sneezes, droplets containing the bacteria or viruses can be inhaled by others.
- Direct contact: Touching surfaces contaminated with respiratory secretions and then touching the face can lead to transmission.
Fungal Pneumonia
Fungal pneumonia is generally not contagious. It usually occurs when individuals inhale fungal spores from the environment, and the infection is more likely to affect those with compromised immune systems.
Prevention Strategies
To reduce the risk of pneumonia, especially the contagious forms, consider the following preventive measures:
- Good Hygiene Practices:
- Wash hands frequently with soap and water.
- Use hand sanitizer when soap is unavailable.
- Vaccination:
- Get vaccinated against pneumonia (e.g., pneumococcal vaccines) and influenza.
- Avoid Close Contact:
- Stay away from individuals with respiratory infections.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle:
- Eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and get adequate sleep to strengthen your immune system.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience symptoms of pneumonia, such as a persistent cough, difficulty breathing, or high fever, seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for a better outcome.
Conclusion
In summary, bacterial and viral pneumonia can be contagious, while fungal pneumonia typically is not. Understanding these distinctions helps in taking appropriate measures to prevent the spread of pneumonia and protect yourself and others, particularly vulnerable populations.
Health Talk : Is Bronchitis Contagious?
![]()